The AI Journey: Exploring Origins, Public Sentiments, and Future Horizons

It's been 67 years since the introduction of the term "artificial intelligence" was first coined.
Since then, artificial intelligence (AI) has become integral to our daily lives, reshaping the world with its transformative capabilities. In this exploration, we'll take a brief look at AI's journey, introduce the leading players in today's AI development, attempt to gauge public sentiments, tackle pressing questions, check out real-world AI applications, and leave you with our predictions for the future of this "oh-so-promising" piece of technology.
Let's jump right into it and allow me to state the obvious.
There's never been a time like today.
Opportunities for innovation, collaboration, and positive transformation are more abundant than ever before.
We're in an era of rapid technological advancements. Breakthroughs in renewable energy solutions, blockchain, quantum computing, gene editing, and augmented & virtual reality are ushering us into a future where the boundaries of what's possible continue to expand.
And then there's AI, the most profound catalyst of change in recent memory.
Artificial intelligence is poised to transform how we work and live.
It already does.
The phrase "We're living in a science fiction movie." doesn't seem so far-fetched anymore. We have self-driving cars, smart assistants that manage our calendars and homes, wearable devices that monitor our health in real-time, streaming services that seem to know our next favourite movie and fridges that can take care of grocery recommendations and online ordering.
These are just a few examples of how artificial intelligence has infiltrated and eased our daily lives, offering unprecedented convenience, efficiency, and personalization that we've been craving.
And this is just the tip of the iceberg.
The latest buzz, generative AI, is here to help us out of our creative blocks, produce musical or visual pieces of art (like Google's Bard and OpenAI's DALL-E 2), write the emails we're dreading to compose (Like GhatGPT) and automate various types of mundane, repetitive tasks.
But let's not jump too ahead; we'll get to what the future holds in a minute.
For now, let's briefly examine what made this possible.
The beginning and present of Artificial intelligence
AI's journey into the modern era took its first steps in the 1950s with Alan Turing's groundbreaking paper on machine intelligence.
In his study, the British mathematician explored whether machines could exhibit cognitive abilities and introduced the renowned "Turing test" to evaluate their capacity to display intelligent behavior comparable to, or indistinguishable from, that of a human.
This pivotal moment sparked the beginnings of early AI research.
In the 1950s and 1960s, researchers explored various approaches to AI, including symbolic reasoning, logical inference, and early attempts at machine learning. One of the pioneering events in AI history was the 1956 Dartmouth Conference, where the term "artificial intelligence" was officially coined.
This conference was a crucial turning point that paved the way for further research, collaboration, and the eventual establishment of AI as a dedicated field of study in universities and research institutions.
Early AI systems focused on logic and rule-based reasoning, achieving successes like playing checkers and proving mathematical theorems.
In the 1960s and 1970s, AI research experienced significant growth. It attracted attention from both academia and industry.
But AI's development wasn't linear. Periods of progress were followed by setbacks and shifts in focus. Despite initial optimism, limitations and funding constraints led to what became known as the "AI winter" in the '70s and '80s.
Later, the 90s saw a resurgence fueled by advancements in computing and the rise of machine learning.
Then, in 1997, IBM's Deep Blue defeated chess master Gary Kasparov, the game's reigning champion, and the world realized that thinking machines had left the realm of sci-fi and entered the real world.
Now, AI is suddenly everywhere. It's in the media, your conversations with colleagues and friends, your favourite mobile and web apps, and maybe even your car.
Industry leaders, investors, startup founders, and businesses are eager to embrace AI for its game-changing potential for efficiency improvements, cost savings, enhanced decision-making, and innovation across a wide range of applications.
According to Crunchbase, in 2023 alone, generative AI and AI-related startups raised nearly $50 billion (yes, you read that right) and the numbers are expected to continue growing in 2024.
So this is where we are now.
You're all caught up. But before looking at the major players that dominate the AI field and some real-world applications, let's take a moment to lay down the groundwork and make sure we have a shared understanding of what AI is.
What exactly is artificial intelligence (AI)?
Merriam-Webster Dictionary defines artificial intelligence as:
-
the capability of computer systems to imitate intelligent human behaviour;
-
a branch of computer science dealing with the simulations of intelligent behavior in computers.
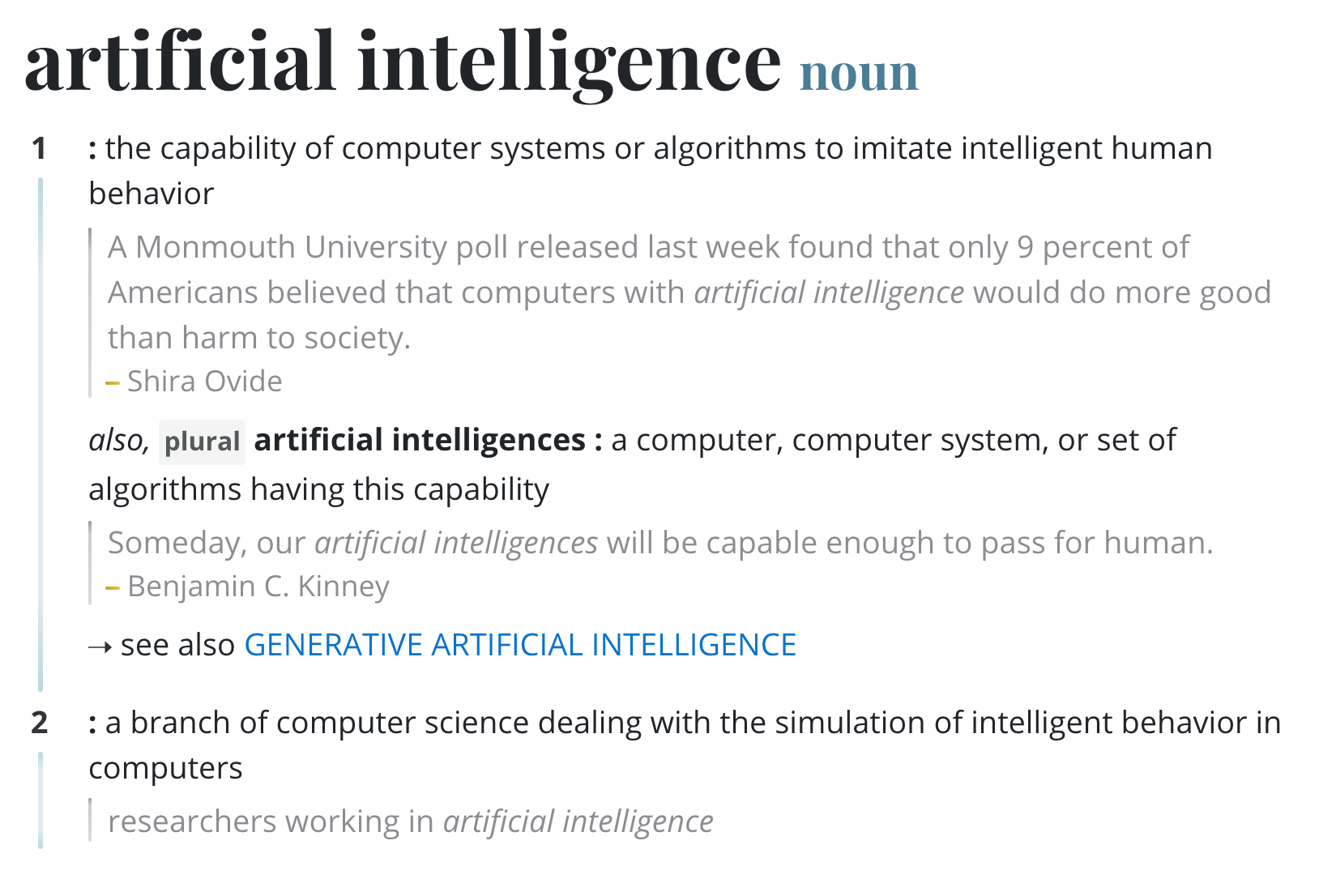
Simply put, AI refers to the development of computer systems that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. These tasks include learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and language understanding.
Essentially, AI aims to create machines capable of mimicking human cognitive functions.
There are three main types of AI: Narrow AI, General AI and Artificial Super Intelligence (ASI).
Let’s take a brief look at them. Don't worry I'll be quick.
Narrow AI (Artificial Narrow Intelligence or ANI):
Also known as Weak AI, this term refers to AI systems that are designed and trained for a particular task or a set of closely related tasks.
These systems are great at what they're made for but don't have the wide-ranging cognitive abilities humans do.
For instance, virtual personal assistants like Siri or Alexa are forms of Weak AI. They can understand and respond to voice commands, provide you with information, and perform tasks like setting reminders, but they are specialized and don't possess general problem-solving abilities.
General AI (Artificial General Intelligence or AGI):
This is the holy grail of AI—a system that possesses the ability to understand, learn, and apply knowledge across a broad range of tasks, much like a human.
General AI, also called strong AI, is still largely theoretical and doesn't yet exist in practice. Kai-Fu Lee, considered the oracle of AI, and founder if more than 140 AI startups, says we won’t achieve artificial general intelligence within the next 30 years and possibly never.
If you've seen the movie "Her", "Ex Machina" or "I, Robot" you can form a pretty good idea about artificial general intelligence. These films explore various aspects of AGI.
Artificial Super Intelligence (ASI):
This highly speculative future possibility takes artificial general intelligence a step further.
Artificial Super Intelligence surpasses human intelligence in all aspects, understanding and performing any intellectual task better than any human.
For now, this is purely hypothetical, but data scientists and AI researchers are investigating the theory and its broader implications.
Artificial Intelligence vs. Machine Learning vs. Deep Learning vs. Neural Network: What’s the difference?
There is a lot of confusion surrounding the AI-related vocabulary.
A lot of different people have different ideas as to what these terms mean and how they relate to each other.
To clear the air a little bit without getting into too many details, I find it's best to look at them as a series of AI systems from largest to smallest, each encompassing the next.
Artificial Intelligence (AI): This is the big category for all computer systems that can do smart things like recognizing speech or understanding language.
Machine Learning (ML): Machine learning is a type of AI that learns from examples instead of being given specific instructions. It's like teaching a computer by showing it lots of examples.
Deep Learning (DL): Deep learning is a special kind of machine learning that uses really complex "neural networks" to learn from huge amounts of data. It's super good at things like recognizing images or understanding human speech.
Neural Networks: These are the building blocks of deep learning. They're like computer versions of the brain's networks of neurons, helping computers understand and process information.
So, think of it as AI being the big picture, machine learning as a way for computers to learn, deep learning as a powerful type of learning, and neural networks as the tools deep learning uses to learn.
Ok. That's it. Now we're on the same page.
Let's look at who are the players of today's AI race and the pioneers of tomorrow's innovation.
Who are the biggest players in AI?
As you'd expect, Microsoft, Alphabet/Google, and Meta Platforms are the frontrunners in AI research and development. These companies have several AI products and services that are used by millions of people around the world.
Microsoft
Microsoft owns Azure AI, Cortana, and Bing and is also a major investor in AI startups, having acquired a number of AI companies in recent years, including Nuance Communications - a tech company specialized in speech recognition, language understanding, and medical imaging, and GitHub, the popular online software development platform.
These to two deals cost Microsoft a approximately $27.2 billion (Woow!) and reveal, the tech giant's strategic plan to significantly expand its AI capabilities and offerings. The fact that Microsoft announced a multi-year, multi-billion dollar investment in OpenAI further solidifies this perspective.
These investments have the potential to shape the future of technology across various industries.
Alphabet/Google
Alphabet/Google, one of the Big Five technology companies in the U.S. IT industry, operates Google Search, Google Translate, and Google Assistant and has too made some significant AI-related acquisitions.
It acquired companies both for their specific application of AI a certain industry, as well as for their resources and talent that would help Google accelerate development of cutting-edge algorithms.
Among these acquisitions are DeepMind Technologies, a British artificial intelligence research laboratory, Kaggle, a machine learning competition platform and Pixabay the image library that makes for excellent labeled training data for Google's vision and image recognition models.
Meta
Meta Platforms is investing heavily in AI to improve its products and services, which are used by more than 3.5 billion people worldwide.
For example, the company is using AI to personalize ads, detect and remove harmful content, and develop virtual reality experiences.
In past years Meta invested research & development, in areas like computer vision, natural language processing, and robotics; acquired companies like GIPHY (image search) and Ascenta (computer vision) to further its capabilities and talent pool, partnered with academic institutions and research labs like Carnegie Mellon University and OpenAI foster knowledge sharing and joint projects.
What does this trend tell us?
In my reading, the fact that big tech firms are putting a lot of effort and money into AI indicates that they see it as a game-changer, which will affect many different areas of life and business.
Who uses AI? And for what?
Artificial intelligence (AI) holds tremendous potential to boost efficiency, cut costs, and refine decision-making processes. And for these reasons, businesses and individuals are inclined to embrace it and harness its potential.
If we look at the general public, AI use is dominated by Gen Z and Millennials.
Millennials witnessed AI take its first wobbly steps and learned to trust it, integrating it seamlessly into their lives. From work emails to streaming services, AI assistants to smart homes, they use it all with ease.
Gen Z and Alpha are digital natives practically born with smartphones in their hands. Their schoolwork, games, even their social lives are infused with AI, and they're constantly trying out the latest trends, from creating art with AI algorithms to chatting with AI-powered bots. They use ai to learn, play, and connect in innovative ways.
Beyond generations, AI is becoming an integral part of various sectors, revolutionizing the way tasks are accomplished and decisions are made.
Here's a glimpse into how different industries and players leverage it:
In healthcare, artificial intelligence is transforming the way diseases are diagnosed and treated. Doctors now have access to advanced AI tools that analyze medical images, identify patterns, and even predict potential health risks, leading to faster and more accurate diagnoses.
Financial institutions are turning to artificial intelligence to combat fraud and manage risks, using advanced algorithms to detect fraudulent activities, improve customer service, and secure financial transactions in our digital age.
E-commerce giants leverage artificial intelligence to revolutionize the shopping experience. From recommendation engines to chatbots, AI technologies are delivering personalized shopping journeys and optimizing inventory management, transforming how buyers shop and interact with online retailers.
In the manufacturing and logistics sector, artificial intelligence is driving unprecedented efficiency and productivity gains. Predictive maintenance, supply chain optimization, and the integration of autonomous vehicles are just a few examples of how AI is revolutionizing operations, reducing downtime, and maximizing output.
And in the field of education, artificial intelligence is reshaping how we learn and teach. Personalized learning platforms, automated grading systems, and intelligent tutoring programs are empowering students and educators alike, creating tailored educational experiences and more effective teaching methods.
In the technology sector, artificial intelligence is at the forefront of innovation, powering virtual assistants, image recognition, and natural language processing. From Siri to facial recognition, AI technologies are seamlessly integrated into our devices, enhancing user experiences and interactions.
Marketing and advertising agencies are harnessing the power of artificial intelligence to refine their strategies, targeting ads with precision, and analyzing data to gain deeper insights into consumer wants and behaviors. Through AI-driven approaches, marketers can deliver more relevant and impactful campaigns, driving increased engagement and maximizing return on investment.
Government agencies utilize artificial intelligence to enhance safety, efficiency, and resource allocation. AI technology helps they identify and prevent security threats, simplifies administrative tasks, and optimizes the distribution of resources during emergencies.
In research and development, artificial intelligence accelerates scientific research, help in data analysis, and facilitates simulations, thus contributing to faster research processes, data-driven insights, and groundbreaking discoveries.
Within human resources, AI-driven transformations are preparing organizations for the future of work by equipping them with agile recruitment processes, predictive analytics for employee engagement, and adaptive talent management strategies. By embracing artificial intelligence technology, HR professionals can stay ahead of market trends, anticipate workforce needs, and build a resilient and future-ready workforce.
AI Through the Public Lens - Perceptions and Attitudes on a Transformative Technology
As we explore the myriad applications of artificial intelligence, we must also examine the intangible yet crucial factor: how the public perceives this transformative technology.
The way people see artificial intelligence is complex and nuanced.
Some are excited about the potential for more efficiency and innovation. They see the possibilities to break free from creative constraints, automate the mundane, and redefine how we learn and teach.
Others worry about how it might affect job opportunities and ethical issues. On their part, there is a mix of curiosity, concern, and a desire for a better understanding of the implications and impacts of AI on various aspects of life.
A recent survey by The Verge, analyzing 2,000 participants, revealed a fascinating spectrum of emotions. While 21% expressed enthusiasm, 29% admitted to anxiety. Notably, 32% felt a mix of both, highlighting the complexity of public sentiment. Notably, 18% held a neutral stance, adding a layer of diversity to the spectrum of responses.
Let's look at some of the pressing questions on people's minds around artificial intelligence.
Impact and Applications:
-
Will AI replace our jobs? If so, what new jobs will be created?
-
Can artificial intelligence be used to solve major global challenges like climate change or poverty?
-
How will AI impact education, healthcare, and other essential sectors?
-
Will artificial intelligence lead to a future of abundance or scarcity?
-
How can we harness the power of AI for good and mitigate potential risks?
Ethics and Fairness:
-
How can we ensure that AI algorithms are fair and unbiased?
-
What are the ethical implications of using AI in warfare or surveillance?
-
Who owns the data used to train AI, and how is it used and protected?
-
How will artificial intelligence impact privacy and individual freedom?
-
Who is responsible for the actions of AI systems—developers, users, or both?
-
Is responsible AI achievable?
Society and the Future:
-
What will it mean to be human in an AI-powered world?
-
How can we prepare future generations for a world with advanced AI?
-
Will artificial intelligence lead to a loss of human control and decision-making?
-
Can artificial intelligence help us address social inequalities and discrimination?
-
What role should governments play in regulating and governing AI?
-
Can AI gain self-awareness?
Technical Concerns:
-
What are the limitations of current AI technology?
-
How can we ensure the security and safety of AI systems?
-
Can AI achieve true intelligence, or will it always be limited?
-
What are the risks of superintelligence and advanced AI capabilities?
-
How can we prevent AI from becoming a threat to humanity?
The Future of Artificial Intelligence - AI Ventures in 2024 and beyond
The AI landscape buzzes with excitement and innovation, but navigating it requires caution as well. Let's explore the fascinating and sometimes concerning trends shaping the future of AI ventures in 2024 and beyond.
Accessibility and the Democratization of AI:
In 2024, big players like Google and OpenAI are focusing on making generative AI profitable. They're creating easy-to-use platforms for people to build their own chatbots, even if they're not tech-savvy. These chatbots can do more than just text—they can handle images and videos, too.
This year, we'll see more regular folks using AI for practical tasks. With simple tools, anyone can create their own AI applications for different needs.
But there are challenges. AI sometimes makes mistakes or shows biases. And there are security risks, especially if AI is connected to the internet.
To succeed, tech companies need to tackle these issues head-on. They must offer strong support and ensure their AI systems are reliable and secure.
Generative AI is advancing to its next stage: creating videos.
This technology initially focused on making realistic images, but it quickly became common. Now, the focus is on turning text into videos, which presents both opportunities and challenges.
Companies like Runway are leading this development, releasing improved tools like Gen-2, which can create impressive short videos. This progress has even led to the creation of an AI film festival, attracting attention from major movie studios.
Beyond entertainment, generative AI is being used in marketing and training, with tools like Synthesia creating deepfake avatars. However, there are concerns about the impact on actors and ethical usage.
As generative AI continues to evolve, it's changing filmmaking and prompting discussions about its ethical implications.
Robotic Systems for Diverse Tasks
Roboticists are taking inspiration from the success of generative AI to create robots that can handle a wide range of tasks.
Instead of training separate robots for different jobs, researchers are developing one-size-fits-all models, like DeepMind's Robocat and RT-X. These robots learn through trial and error, but lack of data is a challenge.
Lerrel Pinto's team at New York University is tackling this by teaching robots to learn as they go. This approach, already seen in driverless cars, is making robots more versatile and efficient, promising a future where they can handle various tasks with ease.
In conclusion, artificial intelligence (AI) has come a long way since its inception, reshaping our world in profound ways. While embracing its potential, we must also address the ethical and practical challenges it poses. At Wolfpack Digital, we're here to assist businesses in harnessing AI's power for growth and innovation. Reach out to us at contact@wolfpack-digital.com to learn how AI can propel your business forward in today's dynamic landscape.
About Wolfpack Digital 🐺
We are an award-winning web and mobile app development company, from Eastern Europe, with over 140 projects successfully delivered to our partners. Everyday, we are guided by our mission to bring performance and beauty to the world through technology.
We develop apps start-to-end and have extensive expertise in beauty app design and development, fintech app development, healthcare IT solutions, custom website development, cross-platform app development services, and many more.
tech insights & news
Stay up to date with the tech solutions we build for startups, scale-ups and companies around the world. Read tech trends and news about what we do besides building apps.
